|
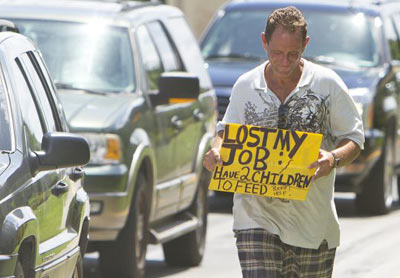 FILE - In a Thursday, Sept. 16, 2010 file photo, a man who did not wish to be identified, who lost his job two months ago after being hurt on the job, works to collect money for his family on a Miami street corner. |
|
The ranks of America's poorest poor have climbed to a record high — 1 in 15 people — spread widely across metropolitan areas as the housing bust pushed many inner-city poor into suburbs and other outlying places and shriveled jobs and income. New census data paint a stark portrait of the nation's haves and have-nots at a time when unemployment remains persistently high. It comes a week before the government releases first-ever economic data that will show more Hispanics, elderly and working-age poor have fallen into poverty. In all, the numbers underscore the breadth and scope by which the downturn has reached further into mainstream America. "There now really is no unaffected group, except maybe the very top income earners," said Robert Moffitt, a professor of economics at Johns Hopkins University. "Recessions are supposed to be temporary, and when it's over, everything returns to where it was before. But the worry now is that the downturn — which will end eventually — will have long-lasting effects on families who lose jobs, become worse off and can't recover." Traditional inner-city black ghettos are thinning out and changing, drawing in impoverished Hispanics who have low-wage jobs or are unemployed. Neighborhoods with poverty rates of at least 40 percent are stretching over broader areas, increasing in suburbs at twice the rate of cities. Once-booming Sun Belt metro areas are now seeing some of the biggest jumps in concentrated poverty. Signs of a growing divide between rich and poor can be seen in places such as the upscale Miami suburb of Miami Shores, where nannies gather with their charges at a playground nestled between the township's sprawling golf course and soccer fields. The locale is a far cry from where many of them live. About 20.5 million Americans, or 6.7 percent of the US population, make up the poorest poor, defined as those at 50 percent or less of the official poverty level. Those living in deep poverty represent nearly half of the 46.2 million people scraping by below the poverty line. In 2010, the poorest poor meant an income of $5,570 or less for an individual and $11,157 for a family of four. That 6.7 percent share is the highest in the 35 years that the Census Bureau has maintained such records, surpassing previous highs in 2009 and 1993 of just over 6 percent. (Read by Lee Hannon. Lee Hannon is a journalist at the China Daily Website.) (Agencies) |
美国极贫人口的比例升至历史新高——15个人中就有1个人极度贫困。这些极贫人口广泛地分布在大都市各个地区中,因为大都市的房市崩溃迫使许多住在市中心贫民区的穷人搬到了郊区和其他边远地区,减少了他们的工作机会和收入。 新的统计数据勾勒出在失业率居高不下的美国,富人和穷人之间反差强烈赤裸裸的现实。将于一周后首次发布的经济数据显示,有更多的西班牙裔人口、老人和劳动年龄贫困人口已陷入赤贫。 总体而言,这些数据突出表明经济衰退的影响已经进一步深入到美国主体,无论是广度还是范围。 约翰•霍普金斯大学的经济学教授罗伯特•莫菲特说:“如今真的没有哪个人群逃过经济衰退的影响,也许只有收入最高的那部分人除外。人们原以为经济衰退是暂时的,在衰退过后,一切都会回到原来的样子。但是现在让人担心的是,尽管经济衰退最终会结束,但是对失业家庭会产生持久的影响,这些家庭会更贫困,而且无法恢复原状。” 传统的市中心黑人贫民区人口正在减少并发生变化,新搬进来一些低收入或失业的赤贫西班牙人。贫困率达至少40%的居民区正延伸到更广的区域,郊区贫民区的增长速度是市内的两倍。 曾经繁荣的“阳光地带”市区正越来越多地陷入集中贫困,部分地区的贫困率是增长最快的。 在迈阿密海岸的迈阿密市郊高档居住区等地方,可以见到贫富差距不断扩大的迹象。那里有大片的高尔夫球场和足球场,保姆们带着主人家的小孩在两个球场中间的一个操场聚集。这个地方和她们当中的许多人居住的地方相比简直是天壤之别。 约有2050万美国人(占美国人口的6.7%)属于极贫人口,也就是生活水平在官方贫困水平的50%以下的人口。在贫困线以下勉强度日的4620万人口中,有将近一半人极度贫困。2010年极贫人口的标准是个人收入在5570美元以下或四口家庭收入在11,157美元以下。 6.7%的极贫人口比例是美国人口普查局保有此项记录的35年内最高的,超越了2009年的高贫困比例,1993年这一比例仅略高于6%。 相关阅读 (中国日报英语点津 陈丹妮 编辑:马文英) |
|
Vocabulary: inner-city: 市中心贫民区 outlying: 远离中心的;边远的 stark: 赤裸裸的;明显的;突出的 underscore: 强调 ghetto: 贫民区 upscale: 高档的;消费对象为高收入者的 charge: 被照顾的人(或事物) nestle: 半隐半现地处于 a far cry from: 同……有很大的差异 scrape by: 勉强过日子,勉强度日 |
